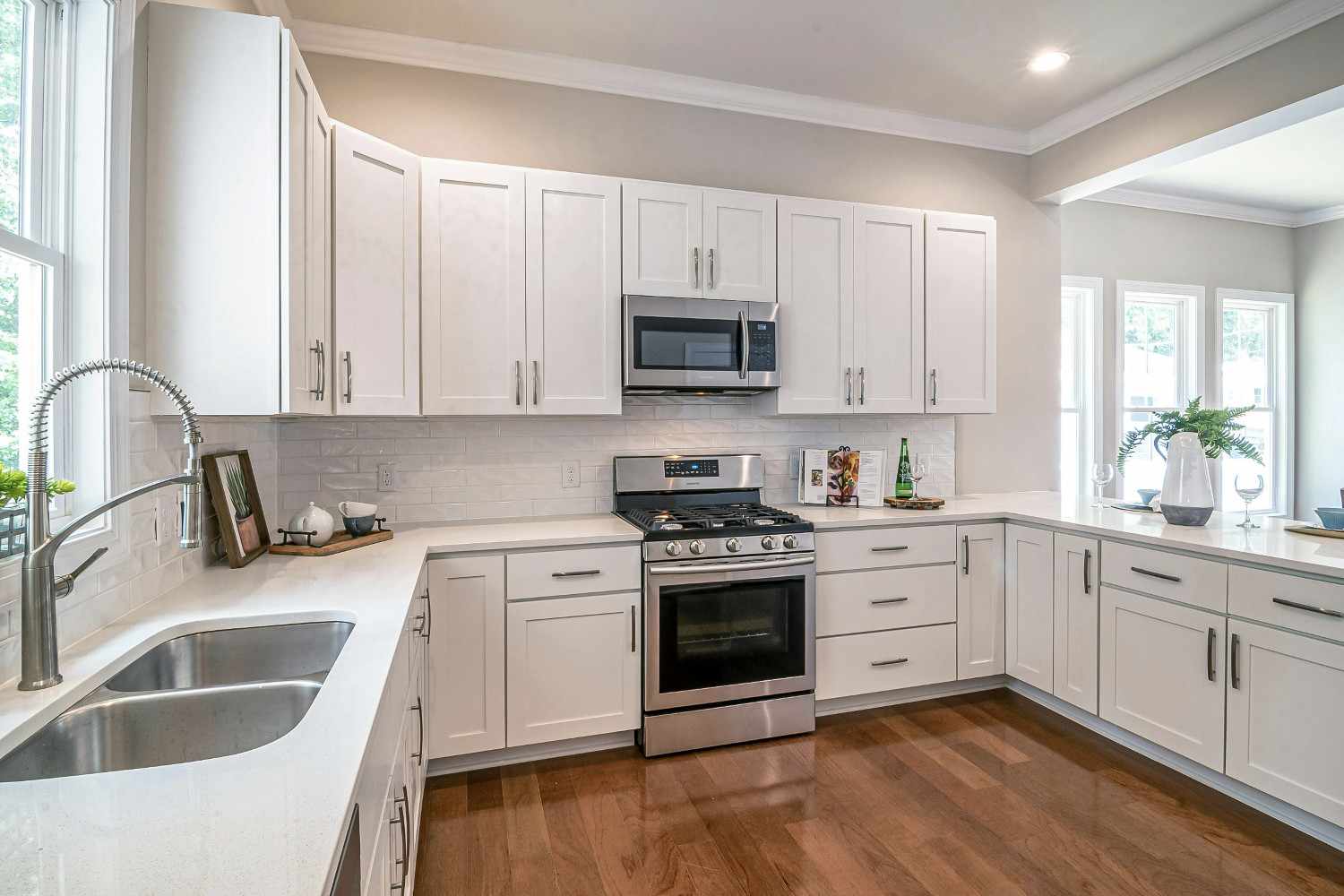
An in-depth roadmap to income for HELOCs
After an almost 13-year decline in popularity, HELOCs are steadily making a comeback. The New York Federal Reserve reported that HELOC balances have ballooned by $3 billion since the first quarter of 2022. Home values rose sharply over those time periods, even while interest rates slowly climbed.
If you’re looking for a way to unlock the equity in your home, but don’t work a traditional W2 job, there are lenders who offer loans called stated income HELOCs to make this happen. Compared to a traditional HELOC which can be hard to qualify for if you’re self-employed, stated income HELOCs don’t require traditional income verification documents, instead, they offer alternative income verification methods.
Before we look at the specifics of stated income HELOCs, we’ll give you a brief overview of HELOCs and how they work, including how they differ from home equity loans and cash-out refinances. Then we’ll dive into stated income HELOCs, how they differ from traditional HELOCs, the pros and cons of stated income HELOCs, and what it takes to qualify for one.
(Please note that we do not currently offer any stated income HELOCs at Defy Mortgage.)
What is a HELOC?
A HELOC, or Home Equity Line of Credit, is a type of revolving credit that is secured by the equity in your home. It allows homeowners to borrow against the equity they have built up in their homes, the difference between the market value (which is determined by an appraisal) and the loan amount.
They became more popular in the last couple of years, due to a massive increase in home equity and all-time-low interest rates. They allow borrowers to keep their original loan rate while providing the opportunity to take out an additional loan equal to the value of their home equity. The additional loan is revolving and uses the home equity as collateral, which typically results in lower interest rates. The credit limit on a HELOC depends on your home’s appraised value. Lenders will use a percentage of the home’s appraised value minus the balance owed on the mortgage to determine the maximum amount you can borrow on a HELOC.
HELOCs can be used in a variety of different ways, including debt consolidation, home renovations, and more. However, since a HELOC uses your home for collateral, it’s important to use the funds responsibly to avoid the risk of losing your home if you’re unable to repay the debt.
A HELOC can help homeowners unlock the equity they have in their homes.
HELOC vs Home Equity Loans vs Cash-Out Refinance
With several different loan types you can choose when it comes to using your home as collateral, it could get confusing and hard to tell the difference between them all. Below, we’ll be covering the main differences between HELOCs, home equity loans, and cash-out refinances.
HELOC
- How does it work? HELOCs use the equity you’ve built in your home to secure a revolving line of credit. Similar to a credit card, you can borrow, repay, and borrow again up to your credit limit during the draw period.
- Interest rate: Interest rates on HELOCs are typically variable and tied to a benchmark rate, such as the prime rate.
- Flexibility: HELOCs are the most flexible loan type out of the three. Since the credit line is revolving, they could be used for ongoing expenses.
Home Equity Loan
- How does it work? A home equity loan is a second mortgage with separate terms from your first. Home equity loans also use the equity you’ve built in your home as collateral for a loan. However, instead of having a revolving credit line, you receive the money in a lump sum and pay the amount back in fixed installments. A home equity loan allows you to access some of the value built up in your property while keeping your original mortgage.
- Interest rate: Interest rates on home equity loans are typically fixed, which allows predictability in monthly payments.
- Flexibility: Not as flexible since a lump-sum disbursement would generally only allow for a one-time expense, such as home renovations or debt consolidation. Unlike a HELOC, there’s no option to repay the amount and borrow it again since payments are fixed for a home equity loan.
Cash-Out Refinance
- How does it work? A cash-out refinance replaces your current mortgage with a new one with a higher loan amount, which allows you to get the difference in cash. Using the cash-out refinance option can be more costly than a HELOC or home equity loan since it requires you to go through the entire closing process again.
- Interest rate: Interest rates for a cash-out refinance can be fixed or variable depending on the terms of the new mortgage.
- Flexibility: Similar to a home equity loan, a cash-out refinance isn’t as flexible due to the lump-sum disbursement along with the monthly payments. However, cash-out refinances can be used to secure a lower interest rate on a mortgage on top of unlocking cash from your home equity and have options for fixed or adjustable interest rates.
Can HELOCs be deducted from taxes?
Depending on what you use a HELOC for, the interest you pay may be tax deductible. Generally, if you use the HELOC funds to improve your home through home repairs or renovations, you can use the interest as a tax deduction.
On top of using your HELOC to make improvements to your home, there are a few other criteria that need to be met to deduct HELOC interest on your taxes, including:
- The home improvements must be on your main home or a second home.
- You must make itemized deductions using Schedule A (Form 1040), Itemized Deductions instead of taking the standard deduction.
- A maximum debt limitation of $1 million ($500,000 if you’re married filing separately) if you took out a mortgage between October 13, 1987, and December 15, 2017. If your mortgage was taken out after December 15, 2017, the debt limitation is $750,000 ($375,000 if you’re married filing separately).
Since taxes can often heavily depend on an individual’s specific situation, if you’re unsure whether you can claim HELOC interest as tax deductions, we would recommend consulting with a tax professional.
If you plan to use your HELOC funds for home improvement, talk to a tax professional to see if you can claim the interest payments as a tax deduction.
Pros and Cons of Going with a HELOC
As great as a HELOC can be for unlocking equity in your home, it’s important to know what the pros and cons are. We’ve outlined the main pros and cons for you below, so you can make an informed decision on whether a traditional HELOC is right for you.
Pros
- Flexibility: HELOCs are incredibly flexible since you can take out money, repay it, and take out money again during the draw period. There are no lump sum disbursements or fixed payment schedules that you need to follow. This way, you have access to the funds when you need it and when you have enough to pay it back, you can pay it back on your own time.
- Interest only accrues on the amount you borrow: Tying into the flexibility of a HELOC, you only have to pay interest on the amount you take out and not on the entire credit line. This means that if you don’t use the HELOC for anything, you won’t be charged any interest. Long repayment terms and low monthly payments.
- Certainty and Options: Fixed rates offer certainty and you have options to use the money from the HELOC however you’d like. Whether it’s to consolidate debt, reduce monthly payments, pay off expenses, renovate your property, etc, the choice is yours.
- Interest paid might be tax deductible: If you use the funds from your HELOC for home improvement, you might be able to claim the interest payments as a tax deduction.
Cons
- Extensive qualification requirements: Lenders that offer traditional HELOCs usually require an extensive list of documentation. It can be difficult to qualify for those who don’t have pay stubs, W2s, or tax returns to prove income.
- Foreclosure risk: Since a HELOC is secured by your home, if you can’t make payments on it, there’s a risk that the lender can foreclose on your home.
- Variable interest rate: Most HELOCs have variable interest rates, which means that market fluctuations can heavily impact how much interest you’re paying.
What is a Stated Income HELOC?
A stated income HELOC is also a type of revolving line of credit that’s secured with the equity in your home. However, with a stated income HELOC, traditional income verification, such as pay stubs and tax returns, isn’t required. Those who apply for a stated income HELOC have to provide proof of income via alternative methods, which makes it easier for self-employed individuals or those who have variable income.
Lenders who offer stated income HELOCs may analyze a borrower’s bank account statements over the past 12 or 24 months to determine their actual income deposits and other factors for qualification requirements. These other factors typically include credit score, assets, and bank statements to determine an applicant’s financial standing.
What is the Difference Between a Stated Income HELOC and a HELOC?
The difference between a stated income HELOC and a HELOC is that a stated income HELOC doesn’t require traditional income verification while a HELOC does.
Typically, to qualify for a HELOC, you’ll need a debt-to-income ratio of 43% or less. Debt-to-income ratio (DTI) measures your monthly debt payments against your monthly income. If you make $70,000 a year before taxes and your monthly debt payments (student loans, car payments, mortgage) are $2,900, your DTI ratio would already be around 50%. You wouldn’t be able to qualify for a HELOC with most lenders.
However, with a stated income HELOC, your DTI doesn’t matter nearly as much, since the lender who offers this loan options considers other documentation that matches your stated income.
Advantages of Stated Income HELOCs
Generally, stated income HELOCs share most of the same advantages of a traditional HELOC, such as flexibility and interest benefits. To differentiate, the main advantage of a stated income HELOC is not having to provide any traditional income verification. If you’re self-employed or don’t have a regular income, a stated income HELOC can allow you to qualify for a HELOC without pay stubs, W2s, or tax returns, but keep in mind that there are some cons.
Some other specific advantages of stated income HELOCs include:
- Provides more accessibility for individuals who want to unlock equity in their homes, but may not qualify for a traditional HELOC
- Faster closing process due to less paperwork required
- Easier approval with a more streamlined approval process
Disadvantages of Stated Income HELOCs
Some disadvantages of stated income HELOCs are:
- Potential for stricter asset requirements to compensate for the lenient income verification requirements
- Potential need for more equity in the home to qualify
- Potentially higher interest rates depending on the lender
- Negative connotation as the term “stated income” played a role in the 2008 financial crisis
- Limited availability and borrowing capacity since not all lenders offer stated income HELOCs
Eligibility Criteria for Stated Income HELOCs
Eligibility criteria for stated income HELOCs may vary depending on the lender you choose to go with and what they offer. Generally, the eligibility criteria that most lenders take into consideration are:
- Stated income: Although stated income HELOCs usually don’t require traditional income verification documents, borrowers need to verify income using alternative methods.
- Credit score: Just like applying for any other type of credit, credit score can be a large factor for qualification.
- Home equity: Most lenders require at least 20% equity in your home.
- Debt-to-income (DTI) ratio: A lower DTI is generally better, but specific DTI requirements will vary between lenders.
- Assets: On top of your home equity, you might be required to have other assets, such as liquid investments, to prove financial stability.
Eligibility criteria will vary depending on the lender.
Common Uses for Stated Income HELOCs
Stated income HELOCs can be used for a variety of different expenses. Some common uses for stated income HELOCs include:
- Home improvement: Any types of renovations, repairs, or upgrades on your home
- Debt consolidation: Transferring other debts to a stated income HELOC to lower the overall interest rate and/or restructure high-interest debt and finances
- Investment opportunities: Using the funds to invest in a second property, expand your business, or diversify your portfolio
- Other large expenses: This could include medical bills, education expenses, wedding expenses, or any other large unforeseen expenses that may come up
Keep in mind that while everyone’s situation is different, it’s important to have a clear plan for what you plan to use the money for and only borrow what you can comfortably repay. Using a stated income HELOC as a blank check for impulse purchases and non-essential expenses can lead to financial difficulties if you don’t have a plan to repay the amount.
Using the funds for home improvement is one of the most common uses for a stated income HELOC.
Stated Income HELOCs and HELOCs: Final Thoughts
Stated income HELOCs can be a great option for individuals with more unique circumstances who want to unlock equity in their homes, but they aren’t the only options. Other options from traditional HELOCs to more evolved non-QM cash-out refinancing options could prove more advantageous for self-employed homeowners. Keep in mind that stated income HELOCs have the potential for stricter asset requirements to compensate for the lenient income verification requirements, potentially higher interest rates, and the potential need for more equity in the home to qualify. Before deciding on your loan option, remember to research lenders thoroughly and have a clear repayment plan.
The onus is on each of us to explore the fuller range of options, even creative alternatives, that align with our deeper life priorities. Non-QM cash-out refinancing options are alternative creative options that homeowners should research and highly consider. These include bank statement loans, profit & loss statements, asset depletion options (great for retirees with liquid assets), DSCR loans and more — all of which we offer at Defy Mortgage.
At Defy, our personalized loan service offers a wide range of competitive loan options to meet your needs. Although we don’t offer stated income HELOCs, we do offer other options for self-employed individuals and other options to tap into your equity for those who currently own. Click here to see how we can help you unlock the equity in your home, and check out some more information on loan options for self-employed individuals.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I get a HELOC without owning a home?
No, You can’t get a HELOC without owning a home. Establishing home equity is crucial for a HELOC.
How is the interest rate for stated income HELOCs determined?
Though the criteria may differ between lenders, generally the interest rate for stated income HELOCs uses the borrower’s credit score, amount of equity in the home, and their stated income.
What are the tax implications of a stated income HELOC loan?
The tax implications of a stated income HELOC can vary depending on how the funds are used. However, generally, the interest on a stated income HELOC can be tax deductible if the funds are used for home improvements or renovations. Consult a tax professional for advice if you’re unsure about the tax implications of your specific situation.
Are HELOCs and home equity loans the same?
No, they are different, however, both require homeownership. As an example of their differences, home equity loans, unlike HELOCs, don’t have the option for borrowers to repay the amount and borrow it again since payments are fixed.
Does a stated income HELOC require tax returns?
No, a stated income HELOC does not require tax returns.
Can I get a stated income HELOC loan with bad credit?
While not impossible, qualifying for a stated income HELOC with bad credit can be very challenging since lenders consider credit score as a significant factor during the approval process.
Are stated income HELOCs fixed-rate?
Stated income HELOCs typically have a variable rate.
What are the interest rates for stated income HELOCs?
While exact interest rates depend on the lender, your credit score, and other approval factors, the interest rates for stated income HELOCs are usually tied to a benchmark or index, such as the prime rate.
Can a stated income HELOC be refinanced?
Yes, a stated income HELOC can be refinanced.
Can you get a stated income HELOC on an investment property?
Yes, it’s possible to get a stated income HELOC on an investment property. However, it’s less common and can be more challenging than getting a stated income HELOC on a primary residence.
What are the down payment requirements for a HELOC?
HELOCs do not require a down payment.
What are the down payment requirements for a stated income HELOC?
Stated income HELOCs do not require a down payment.
Can you get a stated income HELOC with a high DTI (debt-to-income) ratio?
While challenging, it can still be possible to get a stated income HELOC with a high DTI depending on the lender.
What is the application process timeline for a stated income HELOC?
Because stated income HELOCs are more flexible than say, a cash-out refinance, the application process for a stated income HELOC is relatively fast due to less paperwork required and a more streamlined approval process.
Is a Cash-Out Refinance a better option for me than a stated income HELOC?
It depends on your situation. Both a cash-out refinance and a stated income HELOC allows homeowners to access the equity built up in their home, but they have some key differences such as rate options, access differences, approval times, and varying pros and cons to weigh carefully based on your specific financial situation and goals.
Does Defy Mortgage offer stated income HELOCs?
No, we do not. but we do offer purchase and refinancing options for self-employed individuals such as bank statement loans, profit & loss statements, and other non-QM loan options.
Does Defy Mortgage offer HELOCs?
Yes! We do also offer HELOCs, home equity loans and cash-out refinances for those with equity in their home.