How much do houses appreciate per year? The answer can vary significantly due to several factors. Whether you’re a homeowner, real estate investor, or entrepreneur, it’s important to understand how your property appreciates year over year so you can project its equity growth.
At Defy Mortgage, we offer 75+ non-traditional loan options, fully customizable to serve virtually every type of outcome. As non-QM mortgage experts, we have a keen understanding of property appreciation rates and the factors that affect them, so we can help our customers identify investments that have the potential for the best return.
In this blog, we’ll go over how appreciation works and discuss the mechanisms that influence it. We’ll also give you tips on how you can maximize the benefits you can get from appreciation.
Let’s get started!
Average Annual House Appreciation Rates
So, how much do houses appreciate per year? On average, homes in the United States appreciate by 3% to 5% annually, although this can vary depending on location. This means a home purchased for $300,000 could increase in value to between $309,000 and $315,000 within a year. It’s important to note that while long-term trends tend to average out, real estate markets typically have short-term fluctuations year-to-year.
What Is House Appreciation?
House appreciation is the increase in a property’s value over time due to factors such as demand, inflation, and local market conditions. The balance between supply and demand dictates house appreciation–when demand for housing in an area is higher than supply, property value naturally appreciates. Over time, this dynamic contributes to a gradual increase in property value, which is one of the main attractions of real estate investment and home ownership.
How to Calculate Home Appreciation
You can calculate the appreciation rate on your home using the formula below. Be sure to use real data so the estimates can be as accurate as possible:
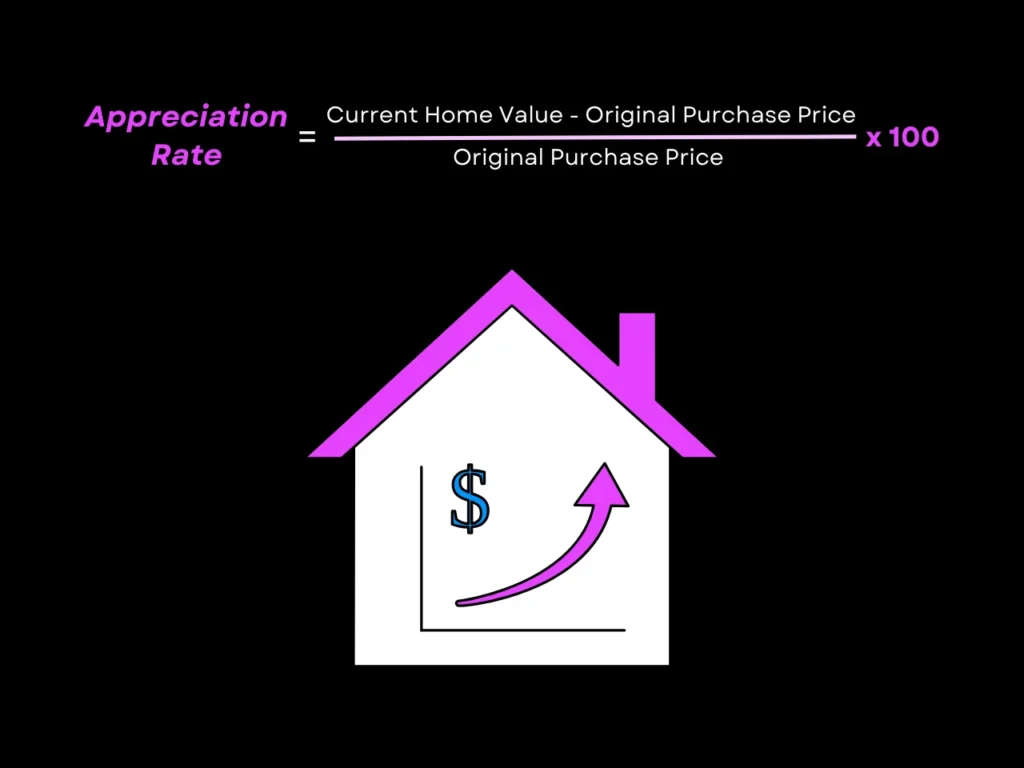
Finding your home’s current value often involves getting an appraisal, but you can work off of a rough estimate taken from similar homes in the area that are in a comparable state in terms of livability and level of improvement. Online tools can provide a quick ballpark, but keep in mind these estimates may not always be accurate. For a more precise valuation, consider consulting a real estate professional who can perform a comparative market analysis (CMA) tailored to your property.
As an example, let’s say you bought a house for $200,000 and its current value after a year is $205,000, the appreciation rate would be:

To get the percentage annual home value increase, simple multiply the rate by 100
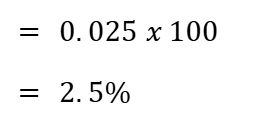
Also keep in mind that appreciation compounds. This means the appreciation rate applies to your home’s total value in any given year and includes any prior increases. For example, in year 3 of the scenario described above, the 2.5% rate will apply to the $205,000 attained in year 2.
To calculate compound appreciation over multiple years, apply the annual appreciation rate using:

Continuing the above example, the value of your property in year 3 would be:
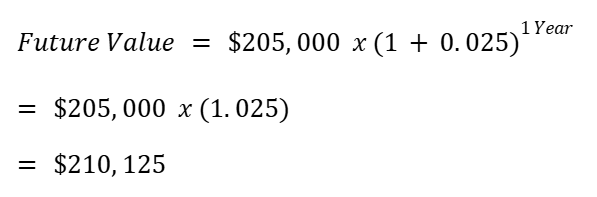
As you can see, as appreciation compounds, it can lead to a large increase in home equity over time. The longer you hold a property, the more significant the impact of appreciation becomes, as each year’s growth builds on the previous year’s gains.
Does the Average Appreciation of Real Estate Have Regional Differences?
While the historic average appreciation of real estate is around 3%-5% in the US, the appreciation rate can vary significantly depending on the region:
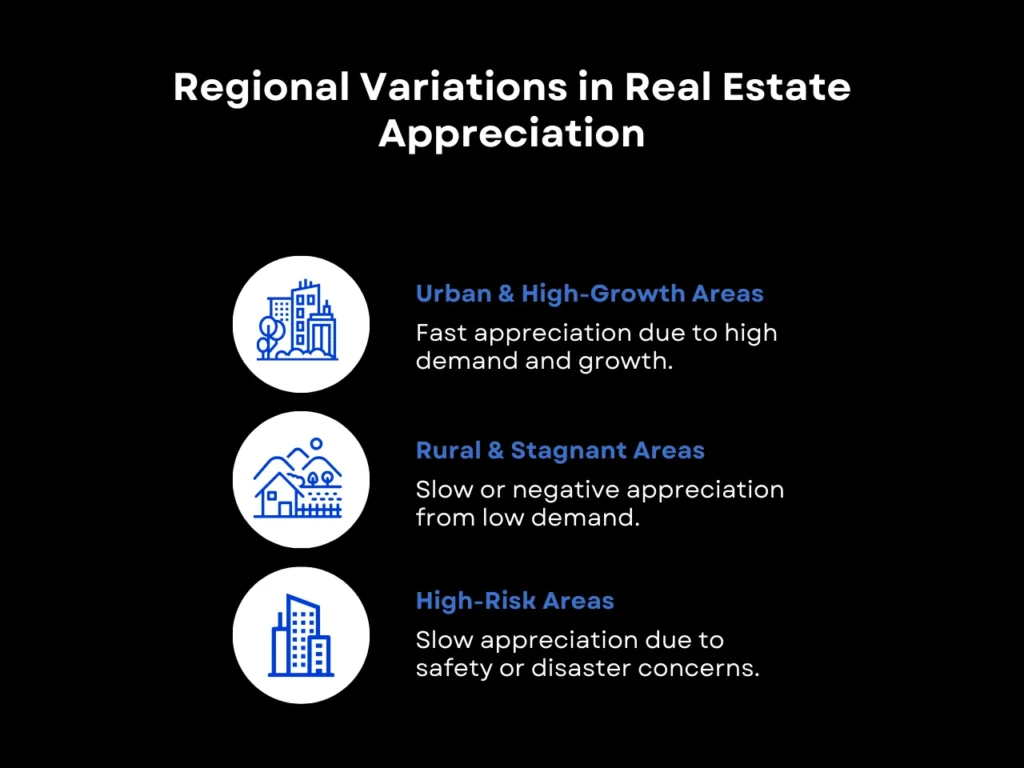
- Urban and High-Growth Areas: Tech hubs like San Francisco and the Bay Area often see appreciation rates well above the national average. These areas attract high commercial traffic but have limited housing supply, driving up property value.
- Rural or Stagnant Areas: Properties in less-developed regions may experience slower appreciation because of slower population growth and economic activity. In some cases, properties may even depreciate if demand declines further as residents leave for better jobs or amenities.
- High-risk Areas: Areas that pose risks to businesses or personal safety, such as disaster-prone areas or cities with high crime rates, can also experience slower property appreciation or depreciation. These risk factors can deter buyers and investors from purchasing available properties, reducing demand.
Rising inflation can also affect real estate appreciation in certain regions by increasing costs but also enhancing property value as a hedge against inflation. As people look to real estate to preserve their financial security, properties in favorable locations can increase further in value, while those in emerging markets may also experience boosts to their appreciation from investors seeking out lower-cost investments.
Factors That Influence House Appreciation
Several factors can significantly influence the rate of your home appreciation over time. These factors shape how attractive your home is to potential home buyers, which is directly reflected in your property value.
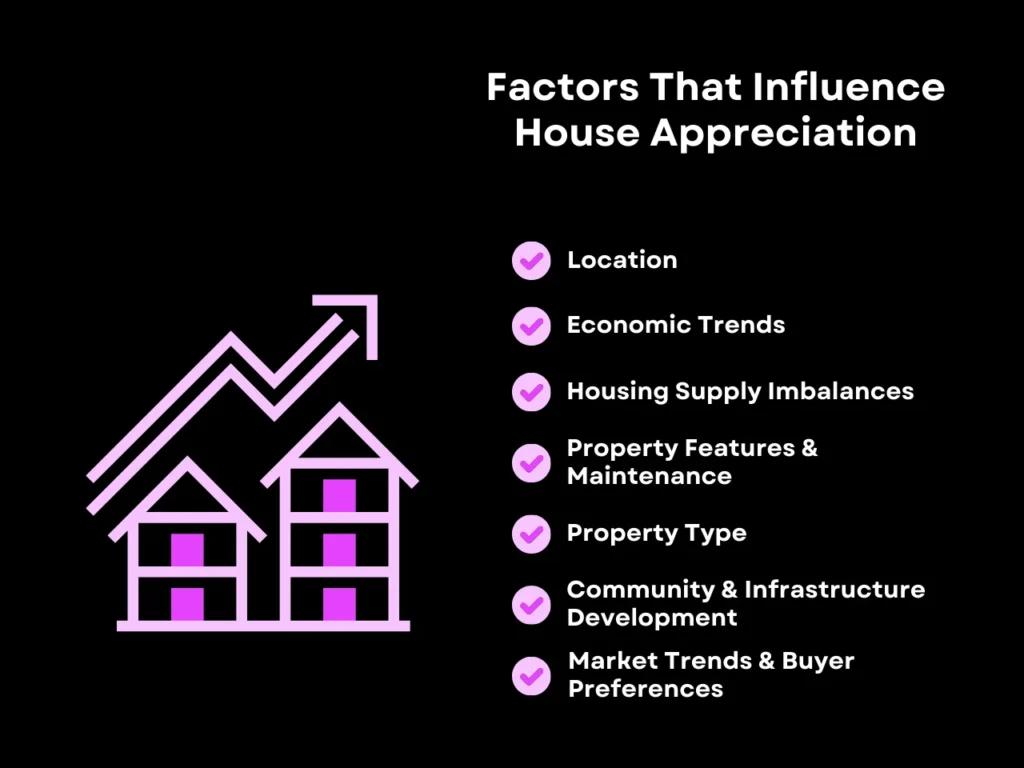
1. Location
Proximity to quality schools, parks, and transportation can significantly boost the value of a property. Neighborhoods with high walkability, safety, and access to urban centers also tend to see higher appreciation. Over the past decade, locational benefits like scenic beauty and cultural and outdoor attractions have elevated growing markets like Nashville, Tennessee, and Boise, Idaho, into highly sought-after locales, with Nashville properties appreciating by 157.1% and those in Boise by 162.5% over the last 10 years, according to NeighborhoodScout.
2. Economic Trends
Economic growth in a region can create demand for housing due to increases in population and jobs, driving up property prices. For example, cities like Austin, Texas, have seen rapid price growth of up to 24% between 2020 and 2021, while areas like Detroit, Michigan, have faced slower appreciation due to economic challenges.
3. Housing Supply Imbalances
In areas with limited housing inventory, high demand often leads to increased property values. Zoning laws and construction rates further impact supply. California is one of the most significant examples of low supply and high demand causing property values to skyrocket. As per the last survey in 2018, California was ranked 49th in the number of housing units per resident among all US states. This has the inverse effect in terms of property value, for which California ranks second.
4. Property Features and Maintenance
Modern features like energy efficiency, updated kitchens, and open floor plans are attractive to buyers and typically enhance value. Regular maintenance, such as timely repairs, also preserves a home’s worth. Homes with desirable features such as energy efficiency often sell for 2.4% more than comparable properties without these features. Neglecting maintenance, on the other hand, could lead to as much as a 10% loss in value.
5. Property Type
Different property types can also appreciate at different rates, with multi-family units potentially having more positive home appreciation in areas where they’re more sought-after, such as university towns or other places where an affordable rental property would be more in demand than single-family detached housing.
The Fayetteville-Springvale-Rogers area, home to the University of Arkansas, is one of the best examples of this. As of the latest data from RealPage in Q4 2022, 97.1% of small apartments in the area, such as multifamily homes, were occupied, exceeding the national average occupancy of around 95%.
6. Community and Infrastructure Development
New infrastructure, such as highways, public transit, and schools, can elevate home values in a community. Nearby commercial or recreational developments also add to a property’s appeal. Properties within a mile of the light rail system in Charlotte, North Carolina, for example, increased in value by 3.4% compared to more distant properties, according to a study by the Journal of Transportation and Land Use in 2012, 5 years after the light rail opened in 2007.
7. Market Trends and Buyer Preferences
Shifts in buyer preferences also influence property appreciation. Some emerging preferences that are dominating home purchase choices include built-in smart home and wellness features or multi-generational living spaces, with 78% of home buyers willing to pay a premium for a home with smart features. Prevailing trends like remote work have also increased demand in suburban and rural areas, but particularly in “exurban” areas that are located just outside city limits. Cities like Haines, Florida saw 30,000 new residents moving to exurban homes in 2023, and the rise of remote work was touted as the primary factor.
Tips to Maximize Home Appreciation
You can maximize your home appreciation by making it as desirable as possible to buyers. By strategically investing in home improvement over time, you can potentially see a strong return on investment through higher property value when you sell. Although we can’t give financial advice, we can share some proven ways that could help raise a home’s appreciation rate:

1. Invest in High-ROI Renovations
One of the most effective ways to increase your home’s value is through targeted renovations and providing upgrades that are consistently in demand, such as adding energy-efficient appliances and quartz countertops, changing to an open-concept layout, or updating bathrooms with contemporary fixtures. These can typically yield a return in the long run by making your home more appealing to future buyers.
In order to maximize your ROI, it is best to align these upgrades with your neighborhood standards. For example, if your neighborhood typically attracts buyers looking for economical choices rather than luxury upgrades, investing in high-end improvements could lead to diminishing returns. Tailoring your upgrades to what buyers in your area value most ensures you get the best bang for your buck.
2. Stay Informed About the Market
Understanding your local real estate market empowers you to make well-timed decisions. Monitoring housing trends, such as average appreciation rates and pricing in your neighborhood, can help you gauge how your previous decisions have affected your property value and identify opportunities to enhance it.
Additionally, research future developments in your area that can add to property demand, such as new schools, shopping centers, or transportation projects. This can give you an idea of how much your property value could grow from neighborhood improvements.
Knowing when to sell is crucial—buying during a market dip or selling when demand peaks can significantly impact your returns. Leverage local market reports or consult real estate experts to stay ahead of the curve.
3. Improve and Maintain Curb Appeal
First impressions matter, and curb appeal plays a pivotal role in determining a home’s perceived value. Even simple external improvements, like a fresh coat of paint, well-maintained landscaping, or replacing old fixtures such as outdoor lights or door handles, can make a big difference.
Beyond maintenance, it’d be prudent to stage your home before an appraisal or viewing. Staging involves deep cleaning, redecorating, and rearranging furniture for maximum aesthetic appeal, allowing you to put your best foot forward for both valuation and attracting potential buyers. This can help eliminate undesirable factors that could compromise your property’s curb appeal, thus supporting a more fair and accurate assessment from appraisers and buyers.
How to Benefit from Real Estate Appreciation with the Right Mortgage
With the right mortgage, you can take full advantage of real estate appreciation that often comes with home ownership. A good mortgage can help you build equity faster, maximize returns, and enjoy the benefit of increased property value without adding financial strain. Here’s how you can approach it:

1. Choose the Right Mortgage Type
The type of home financing you select plays a crucial role in maximizing appreciation. For example, a conventional loan can help you maximize appreciation gains if you have a high credit score, which can significantly lower interest. If your credit score is less than ideal, you can decrease your borrowing costs with FHA loans, which have low down payments, competitive interest rates, and even closing cost assistance for eligible borrowers in states that offer them. Choosing the right mortgage can not only reduce borrowing costs but also expand your options for property types and locations, creating more opportunities to benefit from appreciation potential.
2. Leverage Home Equity
Home equity is the value stored in your home, calculated by taking the difference between your home’s market value and your outstanding loan balance. Since appreciation makes your home more valuable over time, you can own much more in home equity than what you’ve paid on your mortgage so far.
You can tap into your equity through a home equity loan or home equity line of credit (HELOC) to fund high-ROI upgrades that further enhance your property’s value. With a home equity loan, you can also use your equity as a down payment on additional properties, expanding your real estate portfolio and compounding your wealth.
3. Refinance Strategically
If interest rates drop after you secured your original loan, a well-timed refinance lets you secure a lower interest rate than your original loan. This not only improves your financial position but can also free up funds for renovations or upgrades that can increase your property’s value.
You can also take advantage of cash out refinancing, which enables you to access the cash tied up in your home’s value for renovations, investments, or even debt consolidation, all while maintaining ownership.
How Much Do Houses Appreciate Per Year FAQ
What Is the Difference Between House Appreciation and Market Value?
House appreciation refers to the increase in a property’s value over time, while market value is the current price of a home at a given point in time.
How Long Does It Take for a House to Double in Value?

It depends on several factors, and no one can truly predict changing market conditions. However, you can apply the rule of 72 and get a quick estimate of when your investment might double in value.
Can Houses Depreciate in Value?
Yes, houses can lose value due to factors like economic downturns, natural disasters, or declining neighborhood desirability.
Do All Houses Appreciate at the Same Rate?
No, appreciation rates vary by location, property features, and the dynamics of the housing market. Homes in high-demand areas generally appreciate faster.
How to Invest in Houses that Appreciate More Rapidly?
Focus on properties in growing markets with strong economic indicators. Areas that are experiencing increased growth due to migration trends and commercial booms are likely to see higher home values due to increased demand in the future. It can be challenging to tell right away which areas are likely to grow due to economic trends, so speaking to experts is advisable to be fully informed before going through with an investment. Defy’s mortgage experts offer free consultations for all of our potential borrowers – simply book an appointment on our site, call us at (615) 622-1032, or email us at team@defymortgage.com
Key Takeaway
Understanding how much do houses appreciate per year and how various market factors can influence this rate are key to making informed real estate decisions. By considering factors like location, economic trends, and other regional conditions, homeowners and investors can narrow down properties in areas with high appreciation potential.
Once you have purchased your property, you can boost appreciation with useful and aesthetically pleasing home improvements while paying close attention to market trends for signs of further growth or decline.
Curious about your home loan options? Reach out to Defy today to learn about our tailored non-traditional lending solutions. With our seamless platform and competitive rates, we can help you navigate the real estate market with confidence.