For those with unconventional income streams, getting a mortgage can seem unnecessarily challenging. Most traditional mortgages require you to provide pay stubs and W-2s. Without those, your loan application would not accurately reflect your income, especially if you are self-employed individuals, business owners, entrepreneurs, contract workers, or real estate investors.
At Defy Mortgage, we specialize in non-QM products such as bank statement loans, DSCR loans, and P&L loans. With competitive rates, a seamless platform, and highly personalized support, we guarantee a mortgage experience that’s smooth, simple, and stress-free. We can point you to solutions such as Bank statement loans, which allow lenders to look at bank account activity for income verification.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll tell you all you need to know about bank statement loans. We’ll go in-depth into how they work, why they’re such a great option for borrowers with irregular incomes, and what you need to apply.
What are Bank Statement Loans?
Bank statement loans are a type of mortgage that allows borrowers to finance a property purchase using their bank statements as proof of income. This is in contrast to traditional mortgages, which require borrowers to provide W-2s and/or tax returns.
Bank statement loans are considered non-QM (non-qualified) loans and are often provided by alternative mortgage lenders. Typically, borrowers are expected to provide 12-24 months of bank statements to demonstrate cash flow and income from either personal or business bank statement documentation.
Bank Statement Mortgage Loan Rates
Bank statement loan rates can vary based on a variety of factors. These include:
- Credit Score: Most bank statement mortgage lenders generally only work with borrowers with credit scores 620+. However, some lenders may approve borrowers with lower credit scores, although with higher down payments and interest rates.
- Down Payment: The higher the down payment, the lower the risk for the lender, and thus the more likely they are to offer lower rates.
- Loan Amount: Depending on your lender, the total loan amount may or may not impact the loan’s interest rate. Larger loans may be relatively riskier for lenders, so they may sometimes come with higher interest rates.
- Payment structure: Balloon payments, for example, feature large final payments that increase risk and, therefore, potentially lead to higher interest rates. Negative amortization, on the other hand, can increase the total loan balance over time as unpaid interest is added to the principal.
- Home Location: Homes in areas with higher appreciation, such as urban areas in states like Florida and California, can potentially have lower interest rates compared to secondary or tertiary markets.

Fixed-Rate vs. Adjustable-Rate Bank Statement Loans
Bank statement loans can have either fixed or adjustable interest rates. A fixed-rate loan means your interest rate stays the same the whole time you have the loan. An adjustable-rate loan means your interest rate can change over time.
The most common adjustable-rate bank statement loan type is based on the 6-month SOFR (Secured Overnight Financing Rate). This is the interest rate at which banks lend money to each other for short periods, often overnight.
When you get the adjustable-rate bank statement loans, your interest rate typically starts at the current SOFR. The interest rate is then adjusted up or down every six months depending on how the 30-day average SOFR changes. If SOFR increases, your monthly payments could get more expensive.
Depending on your goals, you should choose fixed rate if you want stability and plan to keep the loan long-term. Consider choosing an adjustable rate if you want a lower payment early on and plan to sell or refinance within a few years.
What are the Differences Between a Bank Statement Loan and a Traditional Home Loan?
Bank statement loans have several key differences compared to traditional home loans. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
Traditional Mortgage
- Employment and Citizenship Status: Traditional home loans are intended for individuals who have W-2 income (i.e., a traditional, full-time job) and are U.S. citizens or permanent residents with a Social Security number (i.e., not a foreign national without a green card or other SSN authorized immigration status).
- Credit Score Requirement: Traditional mortgages are intended for individuals with an active FICO credit score and poor to great credit (no bankruptcies or serious credit issues). For example, individuals can apply for FHA loans with credit scores as low as 580. Foreign nationals without FICO credit scores may not be eligible for a traditional mortgage. Conventional loans (not FHA or otherwise government-associated) often require credit scores as high as 700 to qualify for competitive rates.
- Tax Return Requirement: These loans typically require lenders to review tax returns to verify income.
- Down Payment Requirement: FHA, VA, and USDA loans allow borrowers to make extremely low down payments. For instance, FHA loans allow borrowers to qualify with a down payment as low as 3.5%, while VA and USDA loans do not require any down payment. Conventional loan down payments can often be a bit higher, often having a minimum down payment of around 20%.
- Terms: Most regular home mortgages allow borrowers to choose from a wide variety of loan terms, anywhere from a 5/1 ARM (adjustable-rate mortgage), to a 30-year fixed-rate loan.

Bank Statement Loans
- Employment Status: Bank statement loans typically do not require a borrower to have W-2 income or show tax returns. They can be an excellent choice for 1099 contractors, entrepreneurs, small business owners, and others with unconventional income streams.
- Credit Score Requirement: Unlike traditional mortgages, bank statement loans typically do not have a strict credit score requirement. Still, having higher scores can help you get lower interest rates on your mortgage and possibly a smaller down payment. Some lenders, like us at Defy, accept FICO scores as low as 620.
- Tax Return Requirement: Bank statement lenders generally do not look at a borrower’s tax returns or tax statements. At Defy, for example, we don’t require a borrower to show tax returns during the loan qualification process.
- Down Payment Requirement: The down payment for a bank statement loan depends on the lender. At Defy, you can put down as little as 10%. Unlike FHA loans, these loans don’t offer super low down payments like 3.5%, but strong bank statements can help you qualify for lower down payments.
- Other Requirements: Lenders also review additional requirements such as deposit history, cash flow, and steady income for qualification purposes. Consistent income is a key factor in determining qualification.
- Terms: Bank statement loan terms vary significantly by lender. Some offer short-term adjustable-rate loans, while others may offer 30-year (or even 40-year) fixed-rate loans. Certain lenders may offer 10-year interest-only loans.
What Counts as Income for Bank Statement Loans?
Since bank statements contain a wide variety of different transactions, only certain transactions qualify. Typically, only deposits that are regular or recurring over the course of 12 to 24 months, such as rental and business income, are counted towards the borrower’s gross income. This also means that one-time deposits don’t count, as they can give a false picture of the borrower’s average income.
Lenders may also look at your withdrawals, expenditures, and cash reserves in order to gain a full picture of your income.
What Are The Down Payment Requirements For Bank Statement Loans?
Your down payment can also be a major factor in qualification and loan terms. The higher your credit score is, the more likely a lender would be willing to reduce your minimum down payment requirements.
Here’s a rough estimate of minimum down payment requirements depending on your credit score:
- 700+: as low as 10% down
- 660-699: around 15% down
- 620-659: around 20% down or more
What Are The Qualification Requirements For Bank Statement Loans?
Except for income verification, most bank statement loan requirements are similar to those of conventional loans. Here’s what you should consider before applying:
- Do you have a stable income and cash flow? Income reported on W-2s and tax returns is regular and predictable. Since bank statements are going to stand in for that, they must also display a stable history of income over the specified period to establish lender confidence.
- What’s your credit score? Most bank statement lenders require a minimum FICO score of 620, but a higher score can increase the chances of qualifying and getting better loan terms.
- What’s your debt-to-income ratio (DTI)? Lenders consider a DTI of 43% to be the highest one’s existing debt can get while still being able to afford regular bank statement loan payments. Some lenders may go higher.
- Do you have enough for the down payment? Depending on your qualifying income and other criteria, expect to pay at least 20% of the property’s purchase price. At Defy, we offer bank statement loans with as low as 10% down for borrowers with sufficient income.
- Do you have enough cash reserves? If your income, credit score, and DTI are not at ideal levels, lenders may still approve you if you have additional liquid cash reserves to back up payments if any emergencies arise.

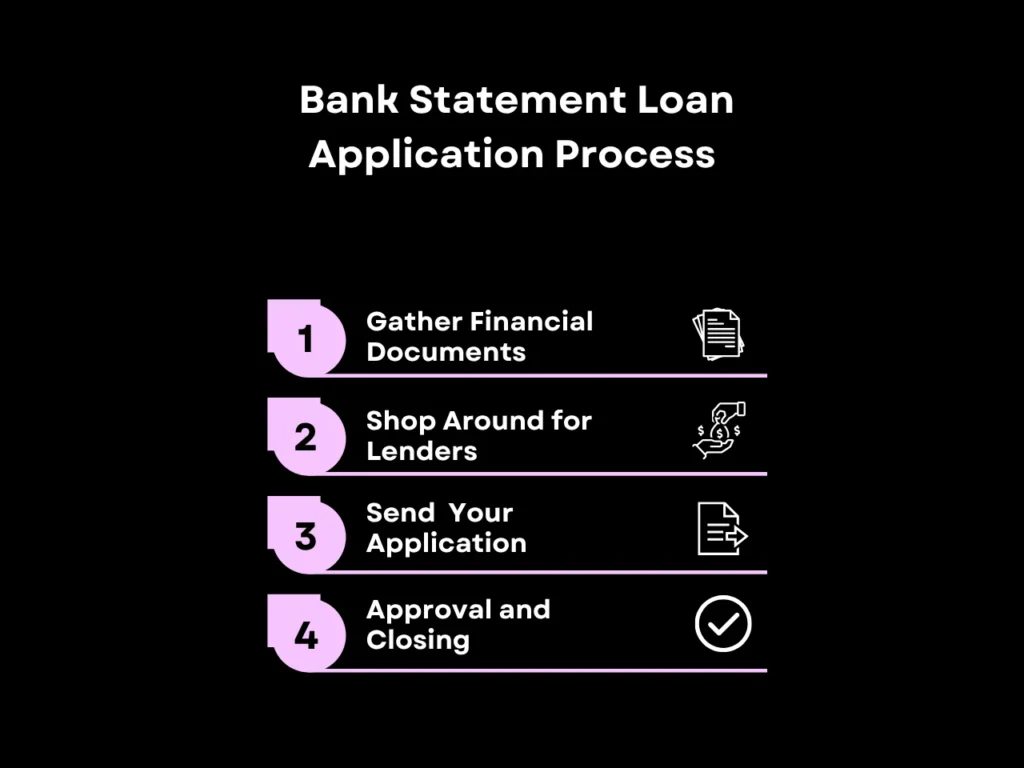
The Bank Statement Loan Application Process
The main difference between applying for a bank statement loan vs. a traditional mortgage is the documentation that’s required for qualification purposes. Below, we’ll walk you through the typical bank statement loan application process:
- Gather financial documents: Prepare 12 to 24 months of personal or business bank statements.
- Shop around for lenders: Not every lender offers bank statement loans. Non-QM specialists (like Defy!) typically offer the best results due to their focus on this category of loans. After you’ve built up a shortlist of lenders that fit your preferences, you can start the pre-approval process with each one to get an estimate on loan amounts and rates.
- Send in your application: Submit a formal loan application to the lender of your choice. They may order a home appraisal to confirm the property’s value, which can affect the initial estimates provided in the pre-approval.
- Approval and closing: If approved, you will receive a loan approval letter from the lender that outlines the terms of the loan, the amount of the loan, the interest rate, the and monthly payment amount. You can then pay the closing costs and officially receive ownership of your new property. Congratulations!
How Are Bank Statement Loans Calculated?
- First, lenders review your bank statements from the past 12 to 24 months and identify deposits that count as income. They may only consider a percentage of those deposits.
- Qualified deposits are totaled and then divided by the number of months to determine your average monthly gross income.
- The underwriters then calculate your DTI ratio by dividing the total monthly debt payments by the average monthly gross income.
- Finally, they look at your credit score, DTI, income, and the property’s value to decide if you qualify. If qualified, you’ll then receive your interest rate and maximum loan amount.
The Pros and Cons of Bank Statement Loans
Pros
- Alternative income verification: For those who don’t work a traditional job that provides them with pay stubs and W-2s, bank statement loans provide them with an opportunity to qualify for a mortgage.
- Flexibility: Since bank statement loans are non-QM, lenders can be a bit more flexible with eligibility criteria and payment terms.
- A wider range of people can apply: Bank statement loans can allow access to homeownership for those who don’t have a traditional income source.
- Faster approval process: Bank statements can give a quicker snapshot of the applicant’s current income compared to tax returns and require less documentation, which can potentially speed up the approval process.
- Possibility of more relaxed DTI requirements: Some bank statement loan lenders allow a higher DTI ratio, which makes it easier to qualify for a mortgage for applicants who have existing debt.
- Larger loan amounts: Bank statements enable lenders to access more accurate income information in comparison to traditionally required documents, which may permit higher loan amounts than traditional loan options.
Cons
- Limited availability: Not all lenders offer bank statement loans. Since bank statement loans are non-QM, they’re more likely to be offered by specialized lenders compared to traditional banks and credit unions.
- Higher down payment requirements: Compared to a traditional loan that can sometimes allow borrowers to put down as little as 3%, bank statement loans typically require between 10-20% down.
- Possibility of higher interest rates: Depending on the lender, bank statement loans may have higher interest rates because of the perceived higher risk than traditional mortgages.
The Different Types of Bank Statement Loans
There are a wide variety of bank statement loan options on the market today, each of which caters to a specific type of borrower. Let’s review some of the most common types:
- Bank Statement Equity Loan and Bank Statement Loan HELOCs: These allow borrowers to withdraw cash from their property’s built-up equity, using bank statement loans as income verification for loan approval.
- Bank Statement Jumbo Loans: Jumbo loans allow borrowers to purchase properties exceeding the conforming loan limits set by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, which is $806,500 for single-family homes in most states as of 2025.
- 6-Month SOFR Bank Statement Loans: Adjustable-rate bank statement loans (ARMs) that adjust every six months based on the current SOFR (Secured Overnight Financing Rate), plus a premium.
- P&L Bank Statement Loans: Allow small business owners and entrepreneurs to have a licensed tax preparer provide their business’s 1-2 year profit and loss (P&L) statement as their proof of income rather than their tax returns.
- Business Purpose Bank Statement Loans: Intended to finance business activities such as employee payroll and marketing. Can come with higher interest rates than regular bank statement loans.
- Personal Bank Statement Loans: Like business purpose bank statement loans, except they are used to pay for personal, non-business expenses. Can also come with higher rates as they are not secured by real property.
- 1099 Loans: Uses 1099 statements as proof of income–ideal for independent contractors who report 1099 income instead of W-2.
Bank Statement Loan Refinancing
If you currently have a mortgage, whether traditional or bank statement, and are looking to refinance or “take cash-out,” bank statement loan refinancing could be beneficial, depending on your circumstances.
One scenario where refinancing from a traditional mortgage to a bank statement loan can be helpful is if you previously worked as a W-2 employee, but have since changed gears to self-employment or entrepreneurship. Refinancing to another traditional mortgage may be difficult without certain documents like pay stubs and W-2s.
A cash-out refinance to a bank statement loan can also help borrowers unlock equity in their home since they can offer up to 90% of a home’s value with no private mortgage insurance (PMI) required. This can help a borrower consolidate debts or free up cash for other purchases, such as home renovations or a new vehicle. Some lenders, like us at Defy, offer high LTV cash-out refinance options with generous cash-in-hand allowances.
Alternatives To Bank Statement Loans
- DSCR Loans: Designed for real estate investing, DSCR loans let you qualify using a property’s cash flow potential rather than your own finances.
- Profit and Loss Statement Loans: Similar to bank statement loans, except these make use of business profit and loss statements to prove income.
- Foreign National Loans: These loans make it easier for foreign nationals to access the US housing market without a US credit score (FICO), green card, visa, or Social Security number.
- Asset Depletion Loans: Asset depletion loans allow borrowers to use their liquid assets, such as stocks and bonds, in place of income. If a borrower has no income but has a significant portfolio of liquid assets, an asset depletion loan can allow them to qualify for a mortgage.
- Interest-Only Loans: Interest-only loans allow borrowers to pay only interest during an initial period of anywhere between 5-10 years, making for more manageable payments early on in the life of the loan.
- Portfolio Loans: Portfolio loans are a type of mortgage where the lender keeps the loan in their own portfolio, rather than selling it on the secondary mortgage market. Since they own the loan, they can be more flexible with the criteria and qualifications. Portfolio loan is an umbrella term and can encompass different loan types.
- FHA Loans: Ideal for first-time homebuyers, allowing as little as 3.5% down and competitive rates, but require mortgage insurance premiums (MIPs).
Bank Statement Loans With Bad Credit
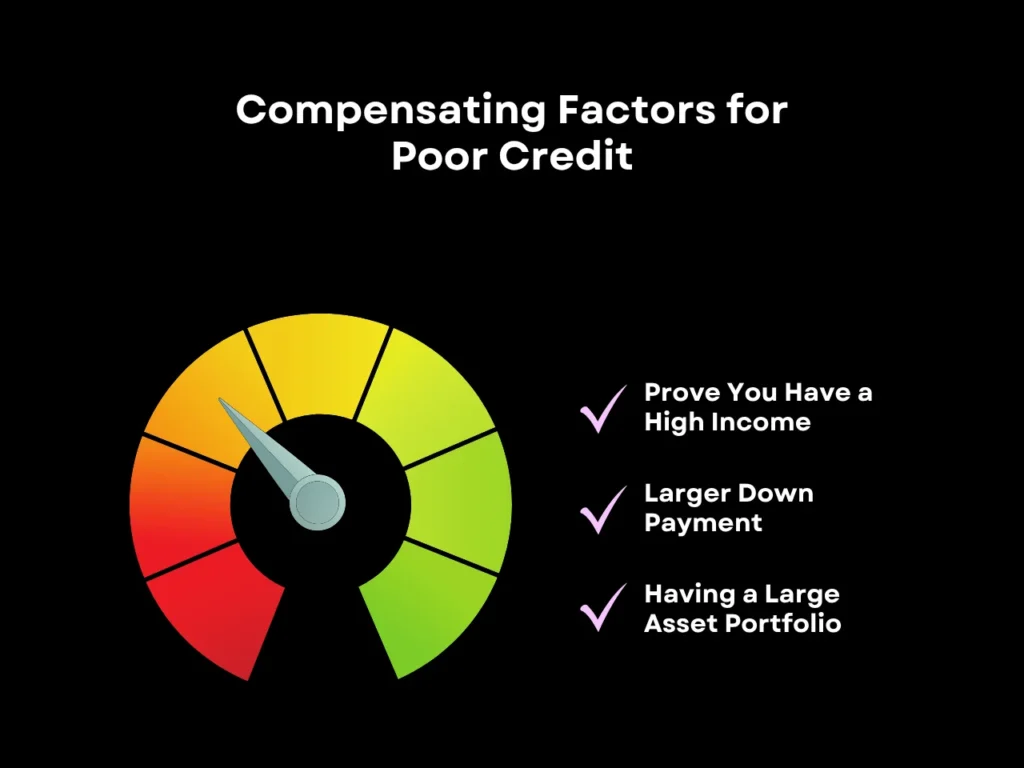
If you have bad credit and are looking to get a bank statement loan, you may be wondering if it’s even possible to qualify. Having a lower credit score can make qualifying for a bank statement loan more challenging, however, it’s not impossible. Here are a few additional factors that a lender may consider to compensate for poor credit:
- Prove you have a high income: If you have poor credit but a high income, demonstrating this to the lender can positively influence your loan application. A high income may offset your credit risk, depending on the lender’s criteria.
- A larger down payment: Making a down payment of more than 20% can reduce the lender’s risk and demonstrate that you are a serious borrower.
- Having a large asset portfolio: Demonstrating to the lender that you possess valuable assets, such as savings and investments, can further strengthen your application.
Always consider taking some time to improve your credit before applying for a mortgage to maximize your chances of securing competitive mortgage rates.
Bank Statement Loan FAQs
Who Does Bank Statement Loans?
Since bank statement loans are considered non-QM loans due to their non-traditional income verification process, they are typically offered by specialized lenders and some mortgage brokers. Though some traditional banks may offer bank statement loans, they often have stricter eligibility requirements.
How Many Months of Bank Statements to Qualify for a Bank Statement Loan?
The exact number of months of bank statements required varies between lenders. However, the general rule of thumb is to prepare between 12 to 24 months of bank statements.
Are Bank Statement Loans Non-Qualified Mortgages?
Yes, bank statement loans are non-qualified mortgages. This is because they don’t follow the strict qualification criteria set by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac due to the non-traditional income verification process.
Can You Get a Bank Statement Loan Without a Bank Statement?
No. Bank statement loans are designed to use your bank statements as a way to verify income when you don’t have W-2s or pay stubs (or when these do not accurately reflect your income). Without these documents, lenders lack the essential information needed to evaluate your financial situation and approve the loan.
Bank Statement Loans vs. No Doc Loans: What’s The Difference?
Bank statement loans utilize bank statements to verify income for self-employed individuals or those with non-traditional income sources.
No-doc loans, on the other hand, require little to no income documentation. Instead, approval is often based on excellent credit, large assets, and a low loan-to-value ratio. These loans usually come with higher interest rates and stricter terms and are very rare today due to tighter lending regulations. We don’t offer no-docs at Defy.

What Is The Minimum Loan Amount For a Bank Statement Loan?
The minimum loan amount for a bank statement loan varies, but typically starts around $100,000 to $175,000, depending on the lender and property type.
Can I Use a Bank Statement Loan on a Second Home?
Yes! You can use a bank statement loan on a second home, such as a vacation home.
Can I Use a Bank Statement Loan on an Investment Property?
Yes! Bank statement loans are a popular option for real estate investors who want to qualify based on cash flow shown in their bank statements.
Are Three-Month Bank Statement Loans Available?
While not common, some specialized lenders might offer bank statement loans based on just 3 months of statements. However, this is typically for exceptionally strong borrowers with high credit scores, low debt-to-income ratios, and significant assets. Expect stricter requirements and potentially higher interest rates compared to traditional 12-24 month bank statement loans.
Who Is A Good Candidate For A Bank Statement Loan?
Bank statement loans are ideal for self-employed borrowers, freelancers, and small business owners whose income is difficult to document via W-2 or tax returns. This includes individuals like entrepreneurs, e-commerce professionals, influencers, retirees, freelancers, and small business owners.
Can self-employed individuals get a mortgage with bank statement loans?
Exactly. Many self-employed individuals lack the standard paperwork, such as W-2s or pay stubs, which makes it challenging to obtain a conventional mortgage. Bank statement loans help by using their bank deposits to prove income instead.
Key Takeaways
If a significant part of your income comes from non-salaried sources, bank statement loans are usually the best way to get a mortgage that most accurately aligns with your financial profile.
While conventional loans offer perks like 3% down payments, bank statement loans also reward strong credit and consistent income, especially for borrowers with higher credit scores or if their bank statements show sufficient incom.
If you’re still unsure about whether bank statement loans are right for you, don’t hesitate to ask our experts over at Defy about your options, such as portfolio loans or DSCR loans, which allow you to qualify using a property’s cash flow potential. We’re here to help!