Real estate financing is the foundation of property ownership.
Andrew Carnegie is famously quoted as saying that 90% of millionaires are made in real estate.
In order to get started on that journey to building your own real estate empire, almost every investor will need financing. Financing provides individuals and businesses with the capital needed to acquire, develop, or refinance properties.
Whether you’re a first-time homebuyer, a seasoned investor, or a developer looking to fund a project, understanding the various financing options available is crucial.
Traditional mortgages, government-backed loans, private lending, and alternative financing solutions — such as non-QM loans — offer diverse pathways to securing real estate funding.
The best choice depends on factors like creditworthiness, income documentation, investment goals, and market conditions.
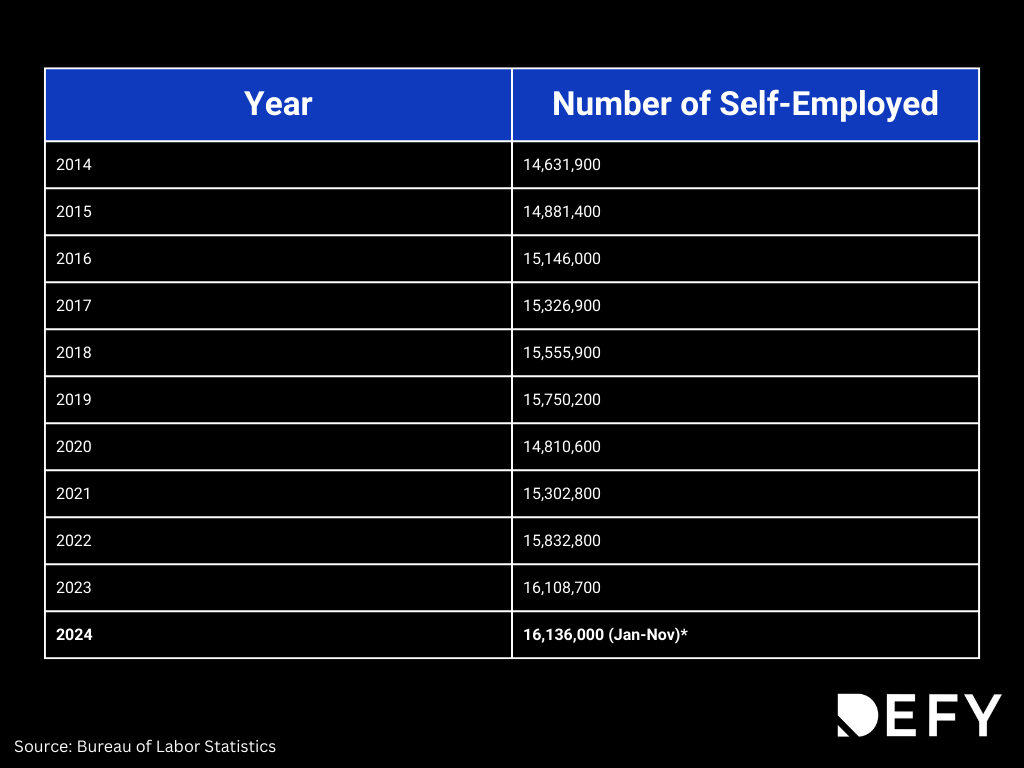
In this day-and-age, with the explosion of freelance work, self-employment, and non-traditional income streams, perfectly qualified buyers and investors are being left behind by traditional lenders. Check out the chart below that we created using data from the US Census Bureau to track the rise in self-employed individuals since 2014:
Additionally, real estate financing varies by state, with regulations, lender requirements, and market conditions influencing available loan products. This guide highlights key financing trends in California and Hawaii — two states with unique market dynamics — while also providing general insights applicable across the U.S.
What Is Real Estate Financing?
Real estate financing refers to the process of securing funds to purchase, develop, or refinance residential, commercial, or investment properties. Lenders provide financing through loans, which borrowers repay over time with interest.
For residential buyers, real estate financing typically involves traditional or government-backed mortgages. Investors often explore alternative solutions such as DSCR loans, hard money loans, or bridge loans to optimize leverage.
Understanding these options ensures borrowers can select financing that aligns with their needs and goals.
Types of Real Estate Financing Options
Traditional Mortgages
Traditional home loans fall into two primary categories:
- Fixed-Rate Mortgages (FRM): Offers stable monthly payments with an interest rate locked in for the loan’s term.
For example, a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage at 7% interest means the borrower pays the same interest rate and monthly payment for the entire 30-year duration, regardless of market fluctuations. This option is ideal for homebuyers who want predictable payments and plan to stay in the home long-term.
- Adjustable-Rate Mortgages (ARM): Features interest rates that fluctuate based on market conditions, often starting lower than FRMs but carrying the risk of increases over time.
For instance, a 5/1 ARM offers a fixed interest rate for the first five years, after which the rate adjusts annually based on market indices. If the initial rate is 4.5%, it may rise or fall after the fixed period, depending on economic conditions. ARMs are beneficial for borrowers who expect to move or refinance before the adjustable period begins.
Here at Defy, we offer both adjustable and fixed rate mortgages on our DSCR products, bank statement loans, profit & loss loans, and asset depletion loans.
Government-Backed Loans
These loans provide financing options with lower down payments and flexible credit requirements:
- FHA Loans: Designed for first-time homebuyers with lower credit scores and down payment requirements.
- VA Loans: Available to eligible veterans and active-duty military personnel with no down payment requirement.
- USDA Loans: Supports homebuyers in eligible rural and suburban areas with low-interest financing.
Hard Money Loans
Short-term, high-interest loans primarily used by real estate investors.
Hard money lenders focus on property value rather than borrower creditworthiness, making these loans ideal for fix-and-flip projects.
However, the interest rates on these loans are typically much higher than many other loan types. Current hard money interest rates (as of 2025, when the average 30-year interest rate is 6.5-7%), range from 10-18%.
Private Mortgage Lenders & Non-QM Loans
- Private Lending: Investors and borrowers who don’t qualify for traditional loans can work with private mortgage lenders for customized financing solutions. As we mentioned at the start of this article, there are a variety of legitimate reasons borrowers might fail to qualify for traditional loan options with many lenders, including self-employment. We can help.
- Non-QM Loans: Ideal for self-employed individuals, investors, and those with non-traditional income, these loans include bank statement loans, asset-based lending, and DSCR (Debt-Service Coverage Ratio) loans.
Home Equity Loans and HELOCs
- Home Equity Loans: Fixed-rate loans that allow homeowners to borrow against the equity in their property.
- HELOC (Home Equity Line of Credit): A revolving line of credit that can be drawn upon as needed, with variable interest rates.
State-Specific Real Estate Financing Insights
California Real Estate Financing
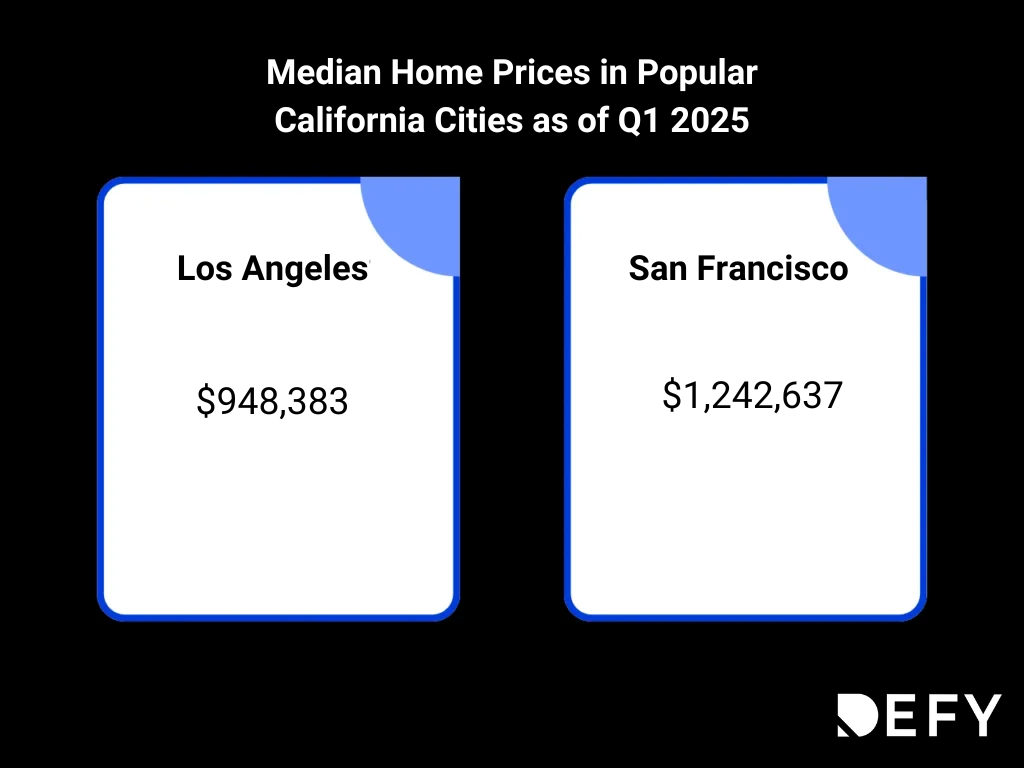
California’s real estate market is known for its high property prices, particularly in major metropolitan areas like Los Angeles and San Francisco. As of today, the median home sells for $948,383 in Los Angeles and a whopping $1,242,637 in San Francisco.
As these home values continue to rise, the demand for jumbo loans has increased, providing financing solutions for properties that exceed conventional loan limits.
To assist first-time homebuyers in overcoming affordability challenges, the California Housing Finance Agency (CalHFA) offers state-sponsored programs that provide down payment assistance and financing options – but these typically aren’t available to high-earners.
Additionally, bank statement loans have become an increasingly popular choice among entrepreneurs and self-employed professionals. These loans cater to individuals who may have strong financials but struggle to document their income through traditional means, offering an alternative pathway to homeownership and investment.
Hawaii Real Estate Financing
Hawaii’s real estate market presents unique challenges due to limited land availability and consistently high demand, which contribute to rising property prices and competitive financing conditions.
To make homeownership more accessible, the Hawaii Housing Finance and Development Corporation (HHFDC) provides state-backed assistance programs aimed at supporting buyers with financial aid and favorable loan terms.
Additionally, Hawaii’s thriving vacation rental and real estate investment market has led to a growing demand for DSCR (Debt-Service Coverage Ratio) loans. These loans are particularly beneficial for investors, as they focus on evaluating a property’s rental income potential rather than the borrower’s personal income, making them an attractive financing option for those looking to capitalize on the state’s lucrative rental market.
Other States
Financing trends and loan availability vary across the country, with states like Texas, Florida, New York, and South Carolina offering unique investment opportunities based on regional economic and housing market conditions.
Asset depletion loans, for instance, cater specifically to retirees or individuals who are not currently working but have significant assets. Instead of relying on traditional income verification methods, asset depletion loans allow borrowers to qualify for financing based on their liquid assets, such as savings, investments, and retirement accounts.
Lenders calculate an applicant’s ability to repay by dividing their total assets over a set period, creating a reliable income stream for loan approval. This option is particularly beneficial for high-net-worth individuals who have substantial reserves but lack a steady paycheck, enabling them to secure financing for primary residences, vacation homes, or investment properties.
Tips for Securing Real Estate Financing
- Improve Your Credit Score to Qualify for Better Rates: A higher credit score can lead to significantly lower interest rates. For example, a borrower with a credit score of 760+ might secure a mortgage rate of 6.9%, while someone with a score of 620 may receive a rate of 7.8%, potentially adding hundreds of dollars to monthly payments.
- Work with a Financial Advisor to Assess Your Loan Options: A financial advisor can help determine the best loan type based on your income, debt-to-income ratio, and long-term goals. For instance, if your DTI ratio is above 43%, lenders may offer fewer options, making strategic debt management crucial.
- Save for a Larger Down Payment to Reduce Loan Costs: A 20% down payment on a $500,000 home ($100,000) eliminates private mortgage insurance (PMI), which can cost between 0.5% and 1.5% of the loan amount annually, saving up to $6,000 per year.
- Compare Lenders to Find the Most Favorable Terms: Interest rates, closing costs, and lender fees can vary widely. Shopping around for lenders could save borrowers 0.25%–0.50% in interest rates, which translates to $50–$100 in monthly savings on a $300,000 loan.
- Understand the Full Cost of Borrowing, Including Closing Costs and Interest: Closing costs typically range from 2% to 5% of the loan amount. On a $400,000 home, that equates to $8,000–$20,000 in fees. Factoring these into your budget prevents unexpected financial strain.
- Consult a Mortgage Broker Familiar with State-Specific Programs: A mortgage broker can guide buyers through programs like CalHFA in California or HHFDC in Hawaii, potentially securing grants or low-interest loans that could save thousands.
- Define Your Real Estate Goals—Whether Investing or Purchasing a Primary Residence: Investors may benefit from DSCR loans, which consider rental income instead of personal income, whereas homebuyers may prioritize fixed-rate mortgages for long-term stability.
Common Challenges in Real Estate Financing
High interest rates can significantly impact borrowing costs, making affordability a challenge for buyers and investors. To mitigate this, borrowers can explore fixed-rate options for predictable payments or consider adjustable-rate mortgages if they plan to sell or refinance before the rate adjusts. Additionally, refinancing when rates drop can reduce monthly payments and overall loan costs, making it a strategic long-term approach.
Strict lending requirements can make it difficult for self-employed borrowers, investors, or those with non-traditional income streams to qualify for loans. Non-QM (Non-Qualified Mortgage) loans provide alternative options, allowing borrowers to qualify based on bank statements, asset depletion, or rental income rather than tax returns. These loans open up financing opportunities for individuals who might not fit into conventional lending criteria.
Securing pre-approval (or rather, failing to secure pre-approval) can also make it more difficult to buy a home. In high-demand states like California and Hawaii, real estate moves quickly, making it essential for buyers to secure pre-approval before searching for properties. Early pre-approval strengthens purchasing power by demonstrating financial readiness to sellers, giving buyers a competitive edge in multiple-offer situations. In order to get preapproved here at Defy, give us a call so we have a better idea of your situation.
Over-leveraging — taking on excessive debt relative to income — can pose significant risks, particularly for investors. Proper financial planning is crucial to ensure cash flow remains positive and manageable. Additionally, buyers should account for closing costs, which can add up significantly. Underestimating these expenses can lead to financial strain or delays in closing.
Conclusion
Understanding real estate financing is key to making informed investment and purchasing decisions. By researching financing options, exploring state-specific programs, and working with industry professionals, borrowers can secure optimal loan solutions for their needs.
Ready to explore your financing options? Contact Defy Mortgage today to learn more about our innovative loan programs tailored to homebuyers and investors.
Real Estate Financing FAQs
What is the best type of real estate financing for first-time homebuyers?
FHA loans, VA loans, and state assistance programs like CalHFA provide accessible options with lower down payments and flexible credit requirements.
What is the best type of real estate financing for real estate investors?
DSCR loans, hard money loans, and non-QM products are tailored for investors focusing on rental income and asset value rather than personal income verification.
How does real estate financing differ in California compared to other states?
California’s high property values necessitate jumbo loans and creative financing solutions like bank statement loans for self-employed buyers.
Are there special programs for real estate financing in Hawaii?
Yes, the Hawaii Housing Finance and Development Corporation (HHFDC) offers state-sponsored programs for affordable homeownership.
Can I get real estate financing with bad credit?
Yes, non-QM loans, hard money loans, and private lending offer financing solutions for borrowers with less-than-perfect credit.
What are the benefits of working with a local lender?
Local lenders provide market-specific insights, customized loan solutions, and a more personalized lending experience tailored to regional conditions.